In the vast tapestry of our natural world, few interactions are as mesmerizing and intricate as those between carnivorous plants and their insect prey. These remarkable plants, with their ingenious adaptations, have fascinated botanists, ecologists, and curious minds alike for centuries. However, beneath the allure of their predatory mechanisms lies a growing concern that threatens their existence: pollution. As we venture deeper into the 21st century, the shadows of human impact loom large over these unique flora. The very survival of insect-eating plants is imperiled by the increasing levels of pollution, a testament to the far-reaching effects of our environmental negligence. 🌍
The allure of carnivorous plants is undeniable. From the iconic Venus flytrap with its rapid snap-trap mechanism to the deceptive beauty of pitcher plants that lure insects into their depths, these species have evolved to thrive in nutrient-poor environments by turning the tables on the traditional predator-prey relationship. Yet, this evolutionary marvel is at risk. Pollutants, seeping into their habitats through air, water, and soil, are disrupting their delicate ecological balance. The chemicals alter the very essence of the environments these plants depend upon, affecting their growth, reproduction, and their ability to capture prey. It’s a silent struggle that echoes the larger story of nature grappling with the consequences of human actions.
The sources of pollution are numerous and varied. Industrial runoff, agricultural chemicals, and airborne pollutants like nitrogen oxides and sulfur dioxide are just a few culprits contributing to habitat degradation. For insect-eating plants, which often inhabit bogs, swamps, and other wetlands, the encroachment of pollutants is particularly damaging. These ecosystems, once pristine sanctuaries of biodiversity, now stand as battlegrounds where the resilience of nature is put to the test. The impact is not just local; it reverberates through the food web, affecting not only the plants but also the insects they prey upon and the broader ecological community.
Yet, amid the dire news, there is hope. As awareness of the plight of these unique plants grows, so does the movement to safeguard their habitats. Conservationists, scientists, and everyday citizens are coming together to combat pollution and its effects. Initiatives to restore and preserve natural habitats are gaining momentum, and innovative technologies are being developed to reduce emissions and clean up contaminated sites. Moreover, public engagement and education are vital tools in this fight, empowering individuals and communities to make informed decisions that can lead to meaningful change.
This article will delve into the fascinating world of carnivorous plants, exploring their biology and the specific challenges they face in polluted environments. We will examine the sources and types of pollution affecting these species and discuss the potential consequences if current trends continue. Importantly, we will highlight the efforts being made to protect these plants and offer practical ways in which readers can contribute to conservation efforts. Whether you’re a seasoned environmentalist or someone newly curious about the natural world, this exploration promises to be both enlightening and inspiring. Join us as we uncover the hidden struggles of insect-eating plants and discover how we can all play a part in ensuring their survival. 🌱
Understanding Insect-Eating Plants
Insect-eating plants, also known as carnivorous plants, have fascinated scientists and nature enthusiasts for centuries. These remarkable plants have evolved to thrive in environments where the soil lacks essential nutrients. By capturing and digesting insects, they supplement their nutrient intake, allowing them to survive and flourish in otherwise inhospitable conditions. Among the most well-known of these are the Venus flytrap, pitcher plants, and sundews. These plants are not just biological curiosities; they play a critical role in their ecosystems by controlling insect populations and contributing to the biodiversity of their habitats.
The mechanics of how these plants capture their prey are as varied as they are intriguing. The Venus flytrap, for instance, uses modified leaves that snap shut when sensitive trigger hairs are disturbed by unsuspecting prey. This remarkable mechanism can discern between living prey and non-nutritional debris, ensuring energy-efficient operation. Pitcher plants, on the other hand, have evolved deep, vase-like structures filled with digestive fluids. Their slick inner surfaces and enticing nectar lure insects to their doom. Sundews use sticky, glandular hairs that ensnare insects, slowly curling around the prey to maximize nutrient absorption.
The evolutionary paths of carnivorous plants are a testament to nature’s ingenuity. Over millions of years, these plants have adapted to their nutrient-poor environments, honing their predatory techniques to near perfection. This evolutionary journey has been driven by the need to survive in harsh conditions, where traditional means of nutrient acquisition are insufficient. By understanding the biology and ecology of these plants, we can appreciate the delicate balance they maintain in their natural habitats and the evolutionary pressures that shaped their development.
The Impact of Pollution on Carnivorous Plants
Pollution poses a significant threat to the delicate ecosystems that sustain carnivorous plants. These plants are often found in bogs, wetlands, and other sensitive environments that are highly susceptible to pollutants such as heavy metals, pesticides, and excess nutrients from agricultural runoff. The introduction of these substances can disrupt the delicate balance of these ecosystems, leading to detrimental effects on carnivorous plants and the broader ecological community.
One of the primary ways pollution affects these plants is through soil and water contamination. Heavy metals such as lead, mercury, and cadmium can accumulate in the soil, poisoning the plants and the insects they rely on for sustenance. Pesticides, although intended to target specific pests, can have broad-spectrum effects, reducing insect populations and thereby depriving carnivorous plants of their primary food source. Additionally, nutrient pollution from fertilizers can lead to eutrophication, a process that depletes oxygen levels in the water and fosters the growth of algae, further altering the habitat.
The indirect effects of pollution can be equally damaging. For instance, changes in climate patterns due to pollution-induced climate change can alter precipitation levels, temperature ranges, and seasonal cycles, impacting the growth and reproduction of carnivorous plants. Acid rain, a byproduct of air pollution, can lower the pH of the soil, making it inhospitable for many plant species, including insect-eating plants. These environmental stressors can lead to reduced biodiversity, compromised plant health, and, ultimately, the decline of carnivorous plant populations.
How We Can Help Protect Carnivorous Plants
Protecting carnivorous plants from the detrimental effects of pollution requires concerted efforts at multiple levels. From individual actions to broader policy initiatives, there are several ways we can contribute to preserving these fascinating plants and their ecosystems. Education and awareness are crucial components in this endeavor. By understanding the importance of these plants and the threats they face, we can foster a culture of conservation and stewardship.
One effective approach is to support conservation initiatives that focus on preserving and restoring the natural habitats of carnivorous plants. Many organizations work to protect wetlands and bogs through land acquisition, habitat restoration, and sustainable management practices. Participating in local clean-up efforts and advocating for the protection of these sensitive environments can make a significant difference. Furthermore, reducing our reliance on harmful chemicals and opting for environmentally friendly alternatives can mitigate the impact of pollutants on these ecosystems.
Policy advocacy is another vital avenue for promoting the health of carnivorous plant habitats. Supporting legislation that limits pollution, enforces environmental regulations, and promotes sustainable land use practices is essential. Engaging with policymakers, participating in public forums, and staying informed about relevant legislation can empower individuals to advocate for positive change. Additionally, research and innovation play critical roles in developing new technologies and methods for reducing pollution and enhancing environmental resilience.
Practical Steps for Individuals
- Educate yourself and others about the importance of carnivorous plants and their ecological roles.
- Participate in local conservation and habitat restoration projects.
- Reduce the use of harmful pesticides and fertilizers in your own garden and support organic practices.
- Advocate for policies and regulations that protect sensitive ecosystems and limit pollution.
For a more in-depth understanding of how carnivorous plants function and their ecological importance, watch this informative video from the Nature on PBS channel.
Comparative Analysis of Pollution Effects
| Type of Pollution | Impact on Carnivorous Plants | Mitigation Strategies |
|---|---|---|
| Heavy Metals | Toxicity in soil and water, leading to plant and insect poisoning. | Implement soil remediation techniques and reduce industrial emissions. |
| Pesticides | Reduction in insect populations, affecting plant nutrition. | Adopt integrated pest management and promote organic farming. |
| Nutrient Runoff | Eutrophication, altering habitat conditions. | Promote buffer zones and sustainable agricultural practices. |
As we explore the intricate relationships between carnivorous plants and their environments, it becomes evident that human intervention can either protect or endanger these unique species. By adopting responsible practices and supporting conservation efforts, we can help ensure that these remarkable plants continue to thrive for generations to come.
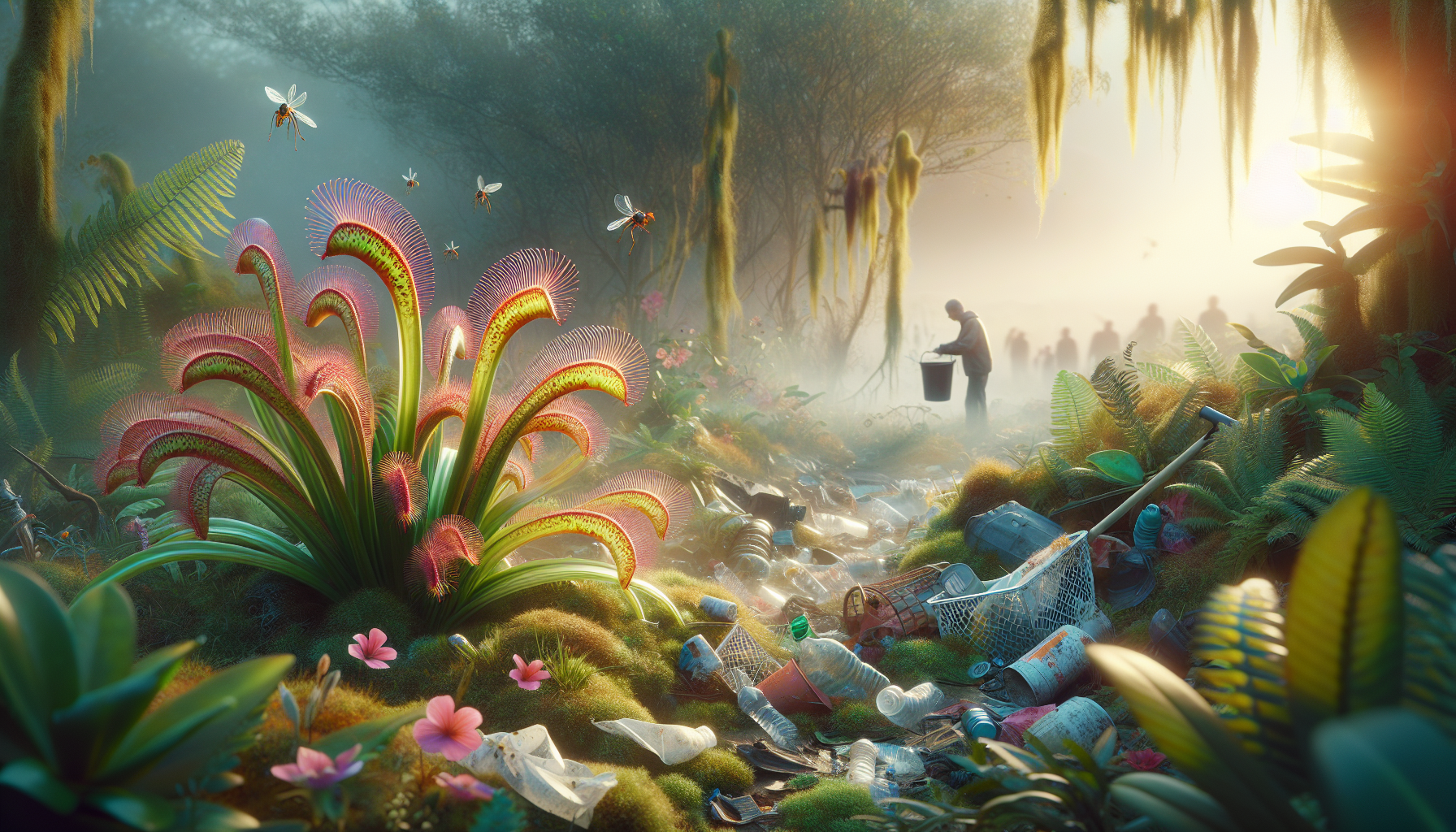
Conclusion
In the intricate tapestry of our natural world, insect-eating plants, often referred to as carnivorous plants, occupy a unique and vital niche. These extraordinary plants, such as the Venus flytrap, pitcher plants, and sundews, have evolved remarkable adaptations to thrive in nutrient-poor environments by deriving essential nutrients from their prey. As highlighted in this article, their well-being is inextricably linked to the broader ecosystem, and yet, these marvels of nature are under threat from an insidious adversary: pollution.
Throughout the article, we explored the multifaceted impact of pollution on insect-eating plants. Pollution, particularly in the form of air and water contaminants, alters the delicate balance of ecosystems where these plants reside. We discussed how pollutants like heavy metals and acid rain can degrade the quality of the soil and water, affecting the availability of nutrients and, subsequently, the health of these plants. Furthermore, the decline in insect populations, exacerbated by pesticide use and habitat loss, reduces the availability of prey for carnivorous plants, further jeopardizing their survival.
One key point addressed is the ripple effect pollution has on biodiversity. Insect-eating plants play a pivotal role in controlling insect populations and contributing to the ecological balance of their habitats. Their decline can lead to overpopulation of certain insect species, disrupting the food chain and causing broader ecological ramifications. This highlights the interconnectedness of all life forms and underscores the importance of preserving these unique species.
The article also delved into the potential consequences of losing insect-eating plants. These plants are not only fascinating for their unique feeding mechanisms but are also crucial for scientific research and education. They offer insights into evolutionary biology, plant physiology, and ecological interactions. The loss of these plants would mean the loss of valuable knowledge and the opportunity to learn from nature’s ingenuity.
In recognizing the threats posed by pollution, the article emphasized actionable steps we can take to mitigate these effects. From reducing the use of pesticides to advocating for stricter pollution controls and supporting conservation efforts, there are numerous ways individuals and communities can make a difference. By promoting awareness and education, we can foster a collective responsibility towards preserving these ecological treasures.
The significance of this issue extends beyond the realm of botany. It touches upon broader environmental challenges that affect all life on Earth. As stewards of the planet, we have a moral obligation to safeguard the diverse forms of life that inhabit it, including the mesmerizing insect-eating plants that have captured our imagination for centuries.
We must also recognize the role of policy and legislation in addressing pollution. Governments and regulatory bodies have the power to implement measures that protect natural habitats and curb pollutants. By supporting policies that prioritize environmental sustainability, we can create a future where both human activities and natural ecosystems coexist harmoniously.
In closing, the plight of insect-eating plants serves as a poignant reminder of the broader environmental challenges we face. It calls us to action, urging us to reevaluate our relationship with nature and to strive for a more sustainable future. The journey to clean up and green up our planet is a collective one, requiring the concerted efforts of individuals, communities, and governments alike.
As you reflect on the insights shared in this article, I invite you to consider how you can contribute to this cause. Whether it’s through personal lifestyle changes, advocacy, or supporting conservation initiatives, every action counts. Share what you’ve learned with others, spark conversations, and inspire change. Together, we can make a difference in preserving the wondrous diversity of life on our planet. 🌿
For further reading and resources, consider exploring reputable sources such as the International Carnivorous Plant Society and Conservation International, which provide valuable information on conservation efforts and ways to get involved. Additionally, you can stay informed about environmental policies through platforms like Environmental Protection Agency.
Let us be inspired by the resilience of nature and work towards a future where both humanity and the natural world can thrive in harmony. Together, we can help protect the insect-eating plants and the myriad of life forms they support. 🌎
Toni Santos is a visual storyteller and botanical artisan whose creations explore the wild elegance of carnivorous and exotic plants. With a deep reverence for nature’s most mysterious flora, Toni captures the untamed beauty of insect-eating mechanisms, alien-like blooms, and resilient life thriving in extreme environments.
Rooted in a lifelong fascination with the strange intelligence of plants, his work blends science, symbolism, and storytelling. From the snap of a Venus flytrap to the labyrinthine curves of a Nepenthes pitcher, each piece Toni creates reveals a deeper narrative — one of survival, adaptation, and the subtle power of nature’s most unexpected designs.
With a background in visual design and handcrafted artistry, Toni merges technique with intention, crafting illustrations, collections, and visual studies that not only depict these botanical wonders — but evoke their hidden magic. His inspiration often comes from ancient lore, natural history, and the eerie elegance of ecosystems where these plants thrive.
As the creative force behind Vizovex, Toni shares this botanical fascination with the world, offering curated artwork, stories, and pieces that help others reconnect with nature’s wilder, more enigmatic side.
His work is a tribute to:
The fierce beauty of carnivorous plants
The visual language of adaptation and survival
The mysteries of exotic flora in forgotten habitats
Whether you’re a plant enthusiast, a science lover, or someone drawn to the strange and beautiful, Toni welcomes you into a world where every leaf hides a secret — one trap, one tendril, one story at a time.





